Public Safety - Chassis Based
Home / Solutions / Public Safety Wireless over Fiber / Chassis Based
Home » Solutions » Wireless Distribution – Cellular and DAS » Public Safety Wireless over Fiber » Chassis Based
BDA(RF Booster) to Active DAS Headend Transport
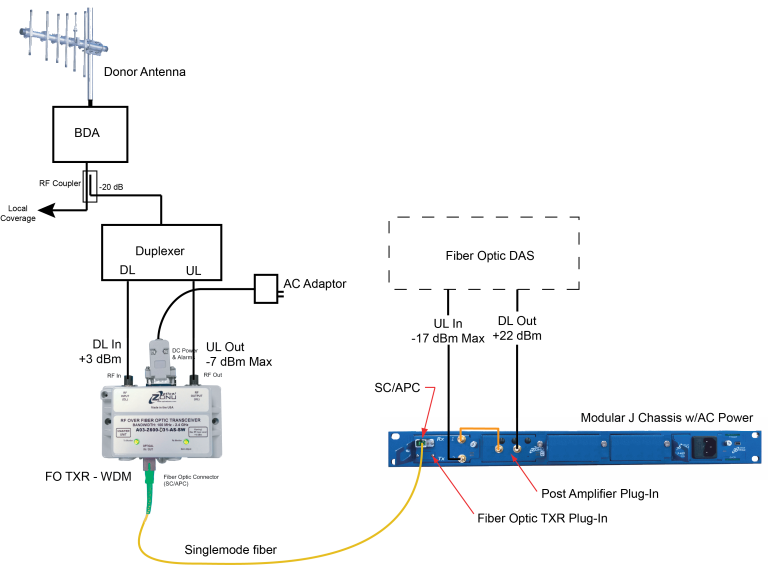
When the off-air donor site is far away, the Antenna Extender may not have sufficient uplink transmit power and downlink sensitivity for a connection of suitable fidelity. In this case, a higher power, low Noise Figure RF booster must be connected directly to the donor antenna. This may mean that the RF booster is far from the DAS headend. Since active DAS typically accepts relatively low RF power and has simplex RF ports, a fiber optic connection between the RF booster and DAS solves the problem.
Optical Zonu offers a range of solutions to satisfy your budget and mechanical requirements.
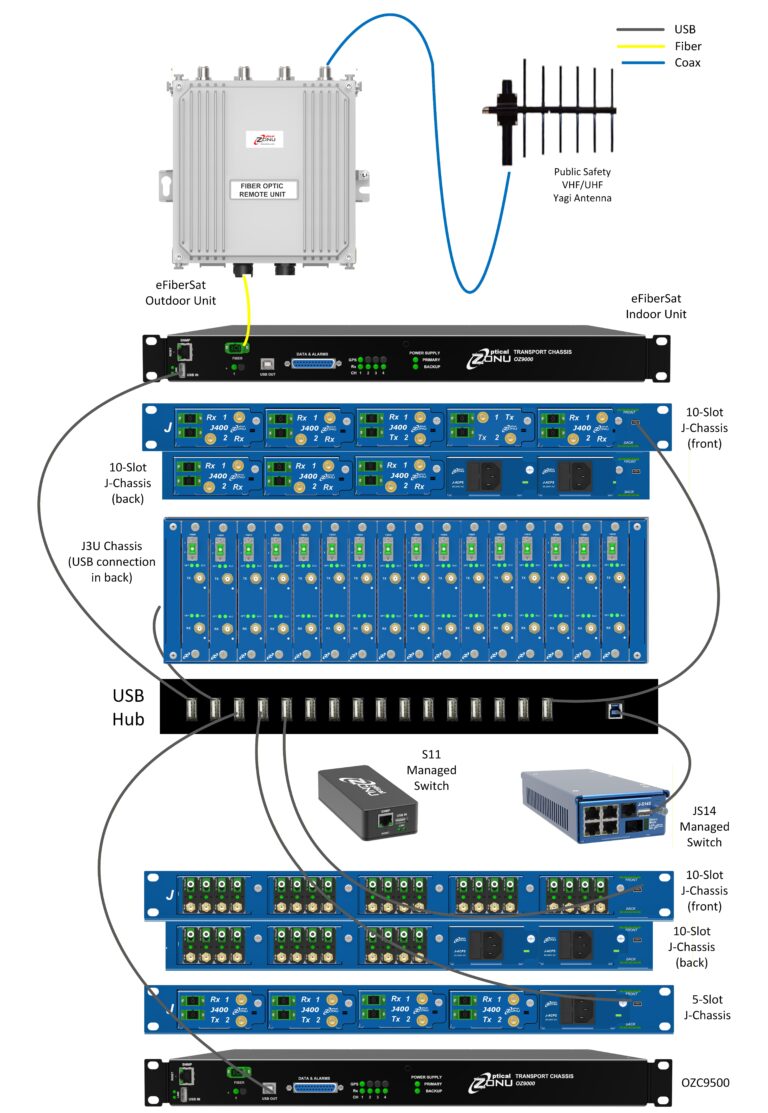
Optical Zonu offers a range of solutions to satisfy your budget and mechanical requirements.
There are numerous Public Safety and Private Radio RF source and booster products that can provide two-way radio service coverage for indoor or blocked locations over coax – but making an efficient connection between these components can sometimes be problematic because of distance or cabling routing issues. Optical Zonu offers a range of RF over fiber optic links that support VHF, UHF, 700 MHz, 800 MHz and 900 MHz. This is a perfect solution for point-to-point and distributed systems for Public Safety, private SMR and government wireless networks.
J Chassis – Modular Rack Mount:
a 1RU (1.75 in) high, 19 in rack mounted modular chassis with 5 plug-in slots. One slot is generally used for a DC or AC power supply. The other four slots can be fiber optic transceiver, power amplifier, gain control, filter or splitter/combiner plug-ins.
An example of a J Chassis configuration used in conjunction with an OZ600 transceiver is shown in the drawing. Here, the duplexed coverage signal from the BDA is tapped and split into uplink and downlink paths for connection to the OZ600 module. At the DAS headend, the fiber optic transceiver plug-in converts the signal to RF. The downlink signal is routed to an amplifier plug-in to boost the signal to a level suitable for the DAS.
ZC9500 Fiber Transport:
A fixed configuration in a 1RU (1.75 in high), 19-inch rack mounted chassis. Available with 1, 2, 3 or 4 two-way RF paths. Separate RF In and RF Out ports for each path. Available with simple contact closure alarms or local and remote SNMP computer control and monitoring.
OZ600 Stand Alone Modules:
Compact (3 x 5 in), DC-powered transceivers. A pair of units provides a wideband RF link that covers 100 MHz through 2700 MHz. Each unit is DC-powered with separate RF In and RF Out SMA ports. Available with two single mode fibers or a single fiber with the WDM option.
Base Station RF Distribution
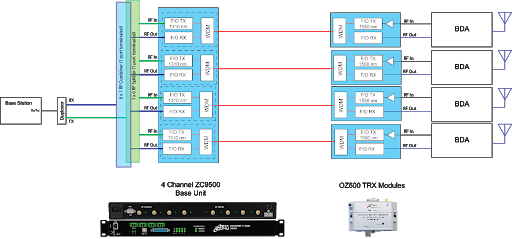
The ZC9500 or J Chassis described above can also be used as a central RF over Fiber hub to simulcast Public Safety RF to multiple remote sites. The OZ600 fiber optic transceiver can be connected to any of the RF boosters from any one of Optical Zonu’s partners, acting as a fiber optic interface that connects to the central hub. When this architecture is applied to simulcasting the macro site, the BDAs indicated would be deployed on multiple towers to guarantee complete coverage. To prevent simulcast interference, the same fiber cable length is used for each site with the excess cable for the shorter runs spooled locally. This ensures that the transit times for the RF signals are identical for each site with the excess cable for the shorter runs spooled locally. This ensures that the transit times for the RF signals are identical for each site.
GPS Fiber Transport
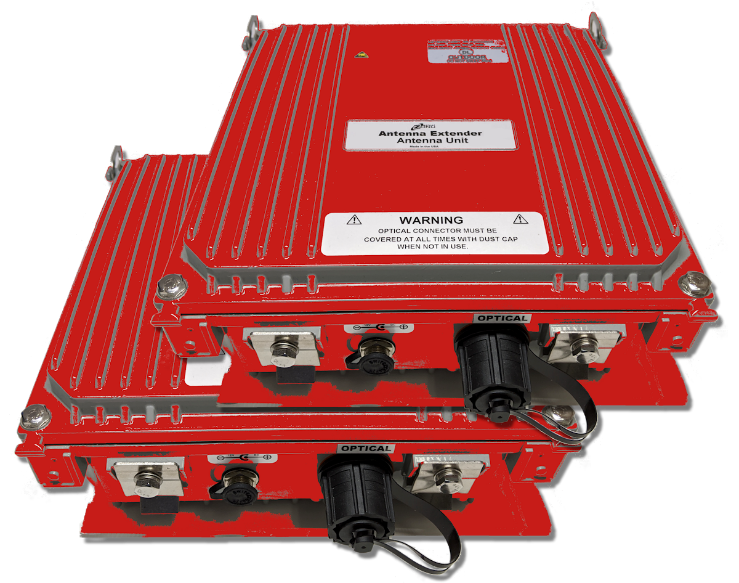
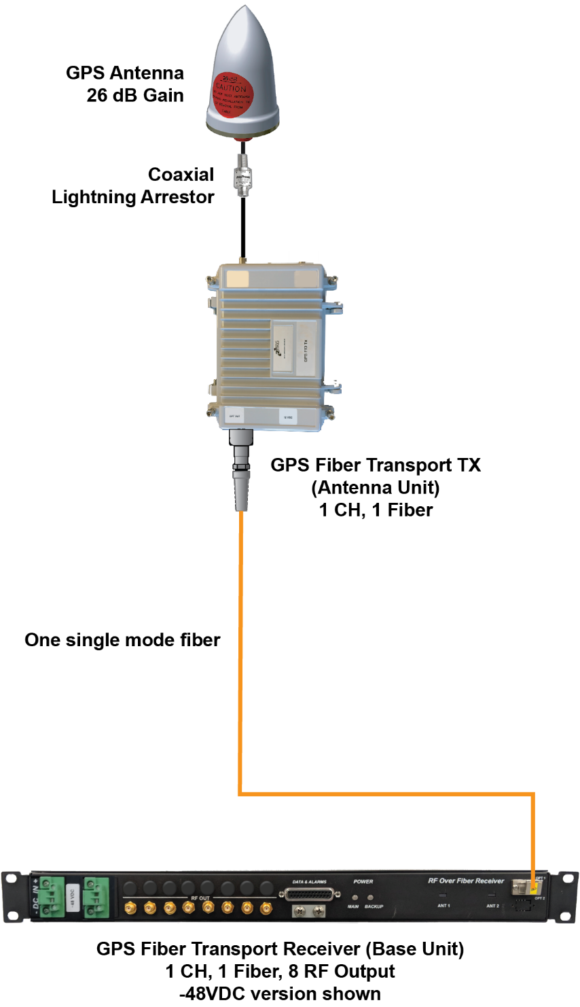
Public Safety communications require accurate timing referenced to a traceable universal time. This is provided by using GPS as the reference. This ensures accurate time stamps on communication events. It also ensures accurate management of talk and listen channels in the network as well as seamless coordination between overlapping networks. The reference is provided by providing a GPS connection directly to the base station radios and by the GPS connection to the Grand Master timing servers in the network. These timing servers generate sync signals that are distributed radios in the network over the backhaul connection to the hub. When these radios and timing servers are installed in the basement far from the building rooftop, a coaxial connection to the GPS antennas is not practical. Optical Zonu solves this problem with the GPS Fiber Transport. The compact (6 x 9 in) Antenna Unit connects to the GPS antenna and can be mounted outdoors or indoors. This unit converts the GPS signal to an optical signal. The Base Unit converts this back to the GPS RF signal for connection to the base station equipment or timing servers. The Base Unit is available with 8 or 16 RF outputs.
Please visit our Blog page by clicking on the articles below
https://www.opticalzonu.com/2020/10/fiber-optic-donor-link-expands-wilson-repeater-applications/
Please visit our Antenna Extender Page by Clicking here
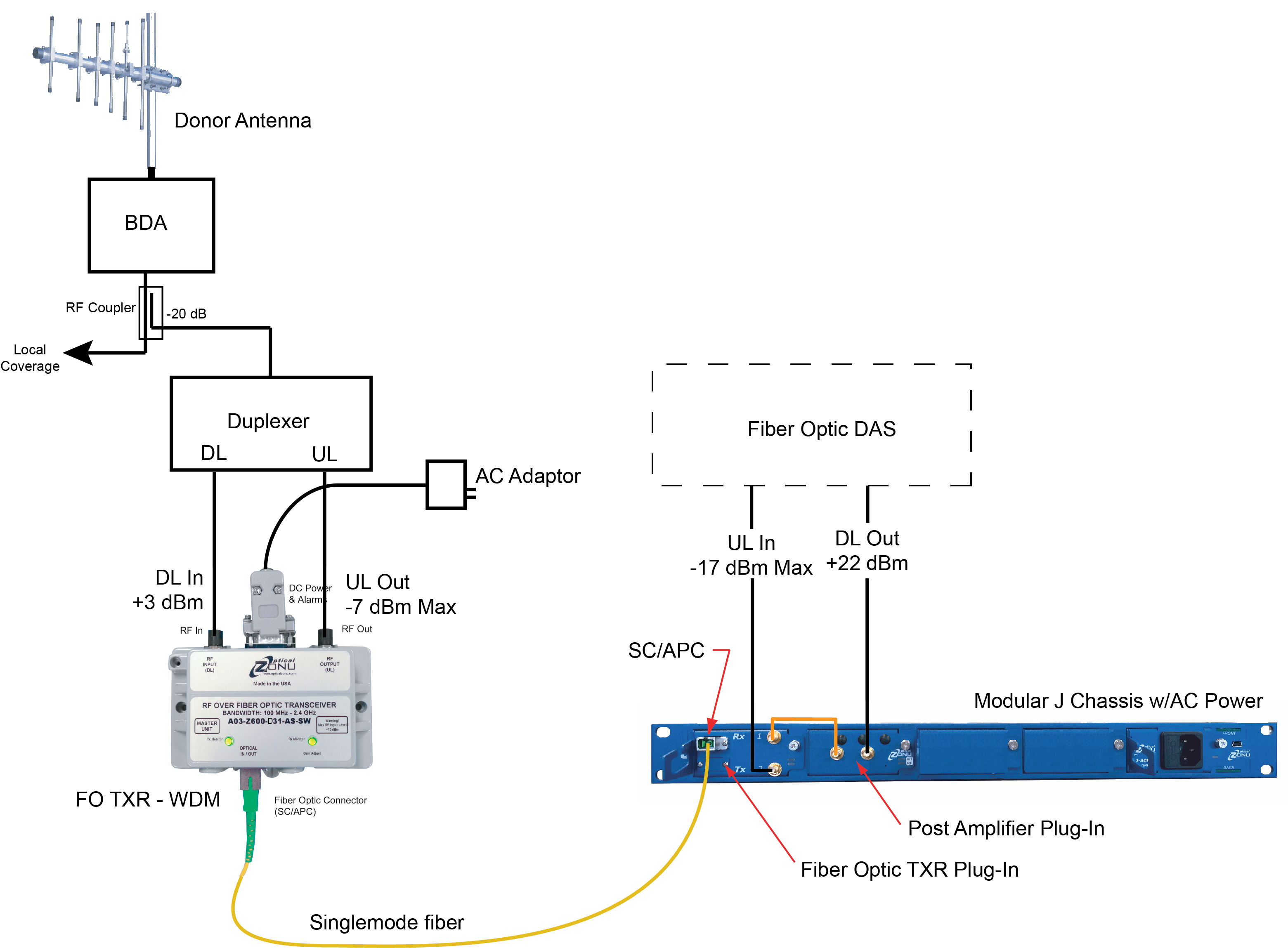
When the off-air donor site is far away, the Antenna Extender may not have sufficient uplink transmit power and downlink sensitivity for a connection of suitable fidelity. In this case, a higher power, low Noise Figure RF booster must be connected directly to the donor antenna. This may mean that the RF booster is far from the DAS headend. Since active DAS typically accept relatively low RF power and have simplex RF ports, a fiber optic connection between the RF booster and DAS solves the problem.
Optical Zonu offers a range of solutions to satisfy your budget and mechanical requirements.
J Chassis – Modular Rack Mount: a 1RU (1.75 in) high, 19 in rack mounted modular chassis with 5 plug-in slots. One slot is generally used for a DC or AC power supply. The other four slots can be fiber optic transceiver, power amplifier, gain control, filter or splitter/combiner plug-ins.
An example of a J Chassis configuration used in conjunction with an OZ600 transceiver is shown in the drawing. Here, the duplexed coverage signal from the BDA is tapped and split into uplink and downlink paths for connection to the OZ600 module. At the DAS headend, the fiber optic transceiver plug-in converts the signal to RF. The downlink signal is routed to an amplifier plug-in to boost the signal to a level suitable for the DAS.
ZC9500 Fiber Transport: a fixed configuration in a 1RU (1.75 in high), 19 inch rack mounted chassis. Available with 1, 2, 3 or 4 two-way RF paths. Separate RF In and RF Out ports for each path. Available with simple contact closure alarms or local and remote SNMP computer control and monitoring.
Base Station RF Distribution
The ZC9500 or J Chassis described above can also be used as a central RF over Fiber hub to simulcast Public Safety RF to multiple remote sites. The OZ600 fiber optic transceiver can be connected to any of the RF boosters from any one of Optical Zonu’s partners, acting as a fiber optic interface that connects to the central hub. When this architecture is applied to simulcasting the macro site, the BDAs indicated would be deployed on multiple towers to guarantee complete coverage. To prevent simulcast interference, the same fiber cable length is used for each site with the excess cable for the shorter runs spooled locally. This ensures that the transit times for the RF signals are identical for each site.with the excess cable for the shorter runs spooled locally. This ensures that the transit times for the RF signals are identical for each site.
GPS Fiber Transport
Public Safety communications require accurate timing referenced to a traceable universal time. This is provided by using GPS as the reference. This ensures accurate time stamps on communication events. It also ensures accurate management of talk and listen channels in the network as well as seamless coordination between overlapping networks. The reference is provided by providing a GPS connection directly to the base station radios and by the GPS connection to the Grand Master timing servers in the network. These timing servers generate sync signals that are distributed radios in the network over the backhaul connection to the hub. When these radios and timing servers are installed in the basement far from the building rooftop, a coaxial connection to the GPS antennas is not practical. Optical Zonu solves this problem with the GPS Fiber Transport. The compact (6 x 9 in) Antenna Unit connects to the GPS antenna and can be mounted outdoors or indoors. This unit converts the GPS signal to an optical signal. The Base Unit converts this back to the GPS RF signal for connection to the base station equipment or timing servers. The Base Unit is available with 8 or 16 RF outputs.
The Antenna Unit is also available with 2 RF connections for a 2nd GPS antenna. In this case, the Base Unit includes an RF switch that selects one signal path as the primary, then flips to the other antenna path if there is any failure on the primary.
For sites requiring more than 16 GPS connections, a 1×2, 1×4 or 1×8 optical splitter can be inserted to route the GPS signal to multiple Base Units.
For sites requiring only one or two GPS connections, a compact (3 x 5 in) GPS Base Unit is available in the OZ600 housing.
Please visit our Blog page by clicking on the articles below
https://www.opticalzonu.com/2020/10/fiber-optic-donor-link-expands-wilson-repeater-applications/
Please visit our Antenna Extender Page by Clicking here